By Gwen Fries, Adams Papers
The news is scary. In the midst of global pandemic, an economic crisis, and nightly images of police brutality, we keep hearing the same question over and over: What do I tell my children?
This is not a new question. Every time John Adams sat at his writing desk in Philadelphia, quill in hand, he contemplated what to say to his “little flock.” He knew they had the violence of war on their doorstep, and the smallpox virus was creeping ever closer. “My Anxiety about you and the Children, as well as our Country, has been extreme,” he confided to Abigail on 24 July 1775.
John recognized that his children were exceptionally lucky to have a mother like Abigail to explain, care, and console, but he was still their father. In his letter to Abigail of 2 June 1775, John wrote, “My Dear Nabby, and Johnny and Charley & Tommy are never out of my Thoughts.”
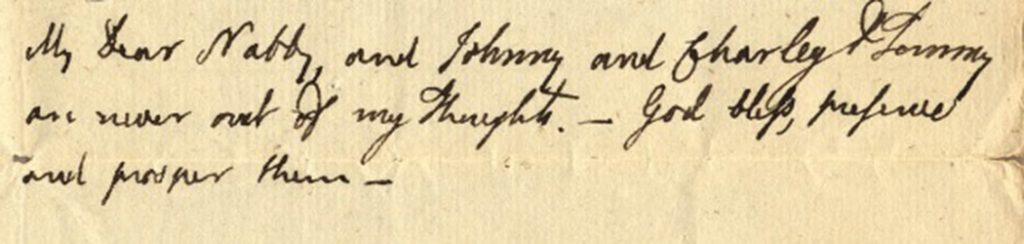
Adams encouraged his children to communicate with him, telling them he longed “to share with your Mamma the Pleasures of your Conversation.” Sometimes he invited the children to lead the conversation and tell him what they were experiencing. On 17 March 1777, he asked his son Charles, “What Subject do your Thoughts run upon these Times. You are a thoughtfull Child you know, always meditating upon some deep Thing or other. Your Sensibility is exquisite too. Pray how are your nice Feelings affected by the Times?”
John also reminded his children that God was watching over them, and that they could trust Abigail to keep them safe. “I hope you and your Sister and Brothers will take proper Notice of these great Events, and remember under whose wise and kind Providence they are all conducted. Not a Sparrow falls, nor a Hair is lost, but by the Direction of infinite Wisdom. Much less are Cities conquered and evacuated,” he wrote to John Quincy on 18 April 1776. For the baby, Tommy, John simply wrote, “Be always dutifull and obedient to your Mamma.”
John Adams encouraged conviction and virtue in his elder children, writing John Quincy what books to pull out of the family library to prepare for a life of public service and responsible citizenship. “Public Virtues,” he wrote to Abigail on 29 Oct. 1775, “and political Qualities therefore should be incessantly cherished in our Children.” For Tommy, who was too young to understand what was happening, John focused on love and play. “Tell Tom, I would give a Guinea to have him climb upon my shoulder, and another to chase him into his Jail.”

John Adams, like every parent, had many anxieties and aspirations for his children. He urged Abigail to “elevate the Minds of our Children and exalt their Courage; to accelerate and animate their Industry & activity— to excite in them an habitual Contempt of Meanness, abhorrence of Injustice and Inhumanity, and an ambition to excell in every Capacity, Faculty, and Virtue.”
To his daughter, Nabby, Adams provided his most succinct advice for navigating tumultuous times: “To be good, and to do good, is all We have to do.”
The Adams Papers editorial project at the Massachusetts Historical Society gratefully acknowledges the generous support of our sponsors. Major funding is provided by the National Endowment for the Humanities, the National Historical Publications and Records Commission, and the Packard Humanities Institute. The Florence Gould Foundation and a number of private donors also contribute critical support. All Adams Papers volumes are published by Harvard University Press.

